What Is Considered the Core Technology of Web 3.0?
2025-04-08 10:58:38
Web 3.0 uses new technology to change the internet, and what is considered the core technology of web 3.0 is blockchain, which is a key part that keeps digital actions safe and clear. Smart contracts build trust by automating deals without middlemen. Decentralized networks give you more control and ownership of your data. The semantic web helps computers understand information better for smarter apps. These tools work together to make the internet safer, fairer, and more open.
What Is Web 3.0 and Its Core Principles?
Decentralization and User Ownership
Web 3.0 gives control back to you, the user. It moves away from big companies owning everything. Instead, it uses systems like blockchain to handle data and transactions. This lets you own your digital identity and assets. For example, DeFi platforms let you manage money without banks. Tokenized assets allow you to own parts of items, opening new ways to invest.
- Benefits of decentralization include:
- Better privacy and security by avoiding central servers.
- Stronger systems with no single point of failure.
- Fairer decisions made by groups, not one authority.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Web 3.0 focuses on keeping you safe and building trust. Blockchain makes all transactions clear and unchangeable. You can check every action without needing middlemen. Decentralized networks lower the chance of hacks by removing central storage spots.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Better Privacy and Security | No central servers mean fewer chances of data leaks. |
| Improved Scalability | Shared systems use many computers for faster performance. |
| Stronger Systems | No single point of failure makes systems more reliable. |
This openness builds trust and makes your experience safer and easier.
The Role of Distributed Consensus in Web 3.0
Distributed consensus is key to Web 3.0. It ensures everyone agrees on transactions. This removes the need for a central authority, making systems faster and more reliable. For example, adding more nodes to a network speeds up processes.
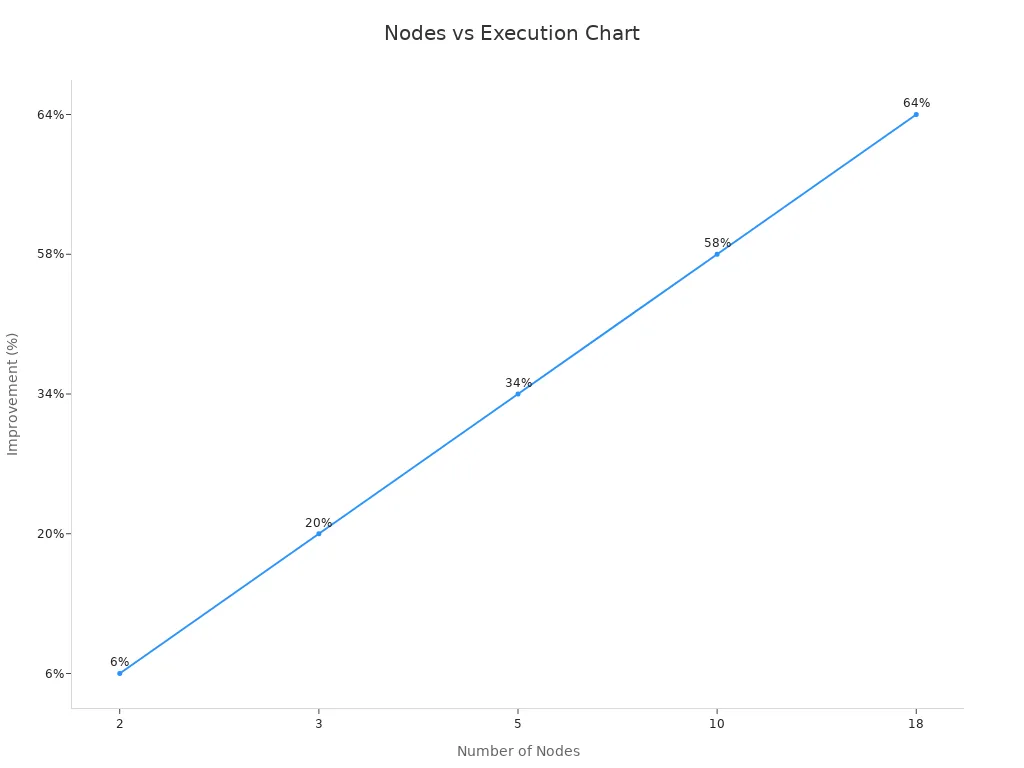
This setup makes networks stronger and scalable. It also lets you help keep the system honest and working well.
Blockchain: The Foundation of Web 3.0

How blockchain enables decentralization and transparency
Blockchain is key to making the internet decentralized. It spreads data across many computers, so no one group controls it. This gives you more control over your digital identity and assets. Blockchain also keeps things clear by recording every transaction on a public list. You can check actions yourself without needing a middleman, which builds trust.
For example, blockchain has changed industries like healthcare and supply chains. It protects data, tracks items, and makes processes clear. In government, blockchain supports fairness by letting people share decisions. But some experts warn about problems like unequal access to technology.
Distributed ledgers and secure transactions
Distributed ledgers are the main part of blockchain. They save data on many computers, lowering the chance of hacks or data loss. This setup removes single points of failure, making systems safer. Transactions on these ledgers cannot be changed or erased. This stops fraud and tampering.
Important blockchain security features include:
- Decentralization: Data is shared across computers, making it stronger.
- Immutability: Records cannot be changed or deleted.
- Encryption: Special codes keep your data safe.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These approve transactions and block bad actions.
- Smart Contracts: Automated deals help prevent fraud.
These features make blockchain a strong base for Web 3.0.
Real-world applications of blockchain in Web 3.0
Blockchain powers many cool tools in Web 3.0. DeFi platforms let you send money directly to others without banks. DAOs allow groups to run projects together without a leader. Apps like Odyssey give you tokens for using content, creating fun ways to earn online.
Here are some examples:
- A digital cat NFT sold for $600,000, showing how valuable digital items can be.
- Gordon Ramsay’s NFTs give 30% off at his restaurants, connecting digital ownership to real-life perks.
These examples show how blockchain is changing industries and opening new doors for you in Web 3.0.
Smart Contracts: Building Trust Automatically in Web 3.0
What are smart contracts and their role in Web 3.0?
Smart contracts are agreements written as computer code. They automatically work when certain conditions are met. In Web 3.0, they help build trust by removing middlemen. You don’t need banks or brokers to finish deals. Instead, smart contracts make sure agreements are clear and secure.
These contracts use blockchain, which makes them safe and unchangeable. For example, in real estate, smart contracts can transfer property ownership after payment is confirmed. This saves time and lowers costs. By automating tasks, smart contracts make Web 3.0 easier and faster for everyone.
Automating transactions and cutting out middlemen
Smart contracts are great at handling tasks without extra help. They save time and money by simplifying processes. Here’s how they make things better:
- They handle financial deals, like stocks, instantly without brokers.
- In insurance, they process claims quickly, making customers happier.
- They reduce mistakes by working without human involvement, saving money.
- Sending money across countries is easier. They handle currency changes and rules automatically.
By doing these tasks, smart contracts make Web 3.0 smoother and cheaper for users like you.
Examples of smart contract uses
Smart contracts are changing how industries work. Here are some examples:
| Industry | Example Company | What They Do |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance | Allianz | Speeds up claims and reduces fraud, building trust. |
| Real Estate | Propy | Makes buying property online faster and skips middlemen. |
| Logistics | DHL | Pays suppliers when deliveries are completed successfully. |
| Mining | BHP Billiton | Ensures suppliers are paid on time with accurate records. |
These examples show how smart contracts improve transparency, cut costs, and boost efficiency. As Web 3.0 grows, you’ll see even more creative ways to use them.
Decentralized Applications: Giving Users More Power
What are decentralized applications (dApps)?
Decentralized applications, or dApps, are programs that use blockchain. They don’t rely on central servers like regular apps do. Instead, they run on peer-to-peer systems, so no one group controls them. This lets you connect directly with others without needing middlemen.
For example, dApps like Uniswap let you trade cryptocurrencies without banks. Platforms like OpenSea allow you to buy and sell NFTs safely. These apps are a big part of Web 3.0, making the internet more open and user-focused.
Benefits of dApps: privacy, control, and strength
Decentralized apps offer many benefits to improve your experience. They protect your privacy by letting you control your data. With blockchain identity tools, you choose what to share and with whom. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) lets you take back access to your data anytime.
Here are some main benefits of dApps:
- You own your data and share less personal info.
- Zero-knowledge proofs confirm details without exposing private data.
- Data is spread across networks, making it safer.
- Blockchain keeps things clear and blocks unauthorized access.
Because dApps run on many nodes, they are strong and reliable. They are less likely to crash or get hacked. This makes your online experience smoother and safer.
Examples of decentralized platforms in Web 3.0
Many decentralized platforms are becoming popular in Web 3.0. They give users new options instead of using centralized services.
| Platform | Registered Users | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mastodon | 15 million | Became popular after changes at Twitter |
| Bluesky | 25 million | Grew quickly after public sign-ups opened |
| 1 million (beta) | Active users during testing phase |
These platforms show how dApps are changing industries and helping users. By using dApps, you get more privacy, control, and safety online.
The Semantic Web: Making Data Easier to Understand
What is the semantic web and why is it important?
The semantic web helps the internet work smarter. It lets computers understand what data means, not just read it. This makes machines process information more like people do. In Web 3.0, the semantic web helps create smarter apps that give better results. For example, search engines can give more accurate answers by understanding what you really mean.
The semantic web is important because it links data from different places. This makes it easier for you to find what you need. It also helps machines work better with data, giving you more personal and useful online experiences.
How does it help machines understand data?
The semantic web helps machines by organizing data clearly. It uses tools like RDF (Resource Description Framework) and OWL (Web Ontology Language) to label and connect data. This helps machines see how pieces of information are related. For example, if you search "best Italian restaurants," it knows you want places to eat, not recipes.
Companies using semantic web tools have seen big improvements. For instance, Spotify’s recommendations made users 26% happier. Adobe got 40% more positive feedback after changing features. These examples show how better data understanding makes users happier.
| Company | What Improved | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | User satisfaction after updates | 24% |
| Adobe | Positive feedback after feature changes | 40% |
| Spotify | Better recommendations made users happier | 26% |
| Slack | Fewer users quit during trials | 18% |
| Slack | More users switched to paid plans | 13% |
How does the semantic web help Web 3.0 apps?
In Web 3.0, the semantic web makes apps smarter and easier to use. It helps platforms understand what you like and show you things you’ll enjoy. For example, shopping sites can suggest items based on what you’ve bought before. Streaming apps can recommend shows you might love.
The semantic web also helps different platforms share data easily. This makes the internet more connected and efficient. By improving how machines understand data, the semantic web helps Web 3.0 apps give you a better and smoother experience.
Practical Applications of Web 3.0 Technologies
Keeping your identity and data safe
Web 3.0 focuses on keeping your data private and safe. Unlike older systems, it lets you control your personal information. You can choose who sees your data and how it’s used. These tools also show you where your data goes, making everything clear. For example, special rules help you track and manage your data securely.
With Web 3.0, you own your digital identity. You don’t need to depend on big companies that might misuse your data. Instead, you can protect your privacy and enjoy a safer online experience.
Changing how we pay and send money
Web 3.0 is improving how we handle money. Digital currencies, like stablecoins, make sending money faster and cheaper. Old payment methods often cost more and take longer. With Web 3.0, you can send money quickly and save on fees.
- Stablecoins are great for sending money across countries.
- Better fraud tools have cut scams by 60% on some platforms.
These changes make sending money easier and safer. Whether paying for services or sending money to family, Web 3.0 makes it simple.
Connecting systems to work together
Web 3.0 helps different systems share information easily. For example, during Israel’s COVID-19 vaccine rollout, health workers used shared data to help people faster. In the UK, a health program collects data to create better treatments.
In Estonia, blockchain keeps patient records safe while sharing them across borders. These examples show how Web 3.0 helps systems work together. By connecting platforms, Web 3.0 makes services better and easier to use.
Web 3.0 changes how you use the internet. It uses blockchain, smart contracts, decentralized networks, and the semantic web. These tools give you control of your data and digital items. For example, DeFi helps people without banks manage money. NFTs let creators earn directly and protect their work. Blockchain keeps healthcare data private and organized. Even schools benefit as students and teachers connect directly.
Web 3.0 makes your online experience safer and clearer. It changes digital ownership and inspires new ideas. These tools will keep growing and give you more control and chances online.
FAQ
How is Web 3.0 different from Web 2.0?
Web 3.0 gives users more control over their data. In Web 2.0, companies manage most information. Web 3.0 uses blockchain and smart contracts to keep things secure. It also makes the internet safer and more open for everyone.
How does blockchain make online data safer?
Blockchain spreads data across many computers to stop hacking. This system keeps your information safe from being lost or stolen. Transactions are locked and can’t be changed, which reduces fraud. Blockchain helps protect your data and builds trust.
Can everyone use decentralized apps (dApps)?
Yes, anyone with internet can use dApps. These apps don’t need approval from a central group. They give you privacy and control over your data. dApps are easy to use and work for everyone.
What are smart contracts, and why do they matter?
Smart contracts are like digital agreements that work on their own. They finish tasks automatically when rules are met. These contracts save time and money by skipping middlemen. They also make deals clearer and reduce mistakes.
How does the semantic web help users?
The semantic web helps computers understand what data means. It gives better search results and smarter suggestions. For example, it can recommend items you might like. This makes your online experience easier and more personal.