What Is the Process of Locking up Cryptocurrency to Support a Blockchain Network and Earn Rewards?
2025-03-11 07:56:10
Staking is the process of locking up cryptocurrency to support a blockchain network and earn rewards. It’s a core feature of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems, where validators are chosen based on the amount of crypto they stake. By staking, users help secure the network and validate transactions, earning rewards in return. These rewards vary by platform, with some offering annual returns as high as 20% or more. Staking is a popular way to earn passive income while contributing to blockchain innovation.
Why is staking gaining traction? Here are some numbers:
Average staking rewards hover around 6.08%, far outpacing the S&P 500's dividend yield of 1.35%.
Some tokens, like Algorand, offer annual returns as high as 84.19%.
Platforms like Cake DeFi provide up to 20% APY with no minimum requirements.
What Is Staking?
Definition and Purpose
Staking is the process of locking up cryptocurrency to support a blockchain network. It plays a vital role in maintaining the network's security and efficiency. Participants, often called stakers, lock their crypto tokens as collateral. This helps validate transactions and secure the blockchain. In return, they earn rewards, usually in the form of additional cryptocurrency.
The concept of staking emerged as a solution to the energy-intensive nature of mining. In 2012, Sunny King and Scott Nadal introduced the proof-of-stake mechanism. A year later, Peercoin became the first cryptocurrency to use staking for transaction validation. This innovation marked a shift toward more sustainable blockchain systems.
Year | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
2012 | Introduction of PoS | Sunny King and Scott Nadal shared the Proof of Stake concept. |
2013 | Launch of Peercoin | Peercoin became the first cryptocurrency to use staking for validation. |
Staking cryptocurrency offers a less resource-intensive alternative to mining. It aligns the interests of participants with the network's growth. By staking, users contribute to blockchain security while earning passive income.
How Staking Supports Blockchain Networks
Staking strengthens blockchain networks in several ways. First, it ensures transaction validation. Staked tokens act as collateral, reducing the risk of malicious activity. Validators who act dishonestly risk losing their staked assets. This encourages integrity and trust within the network.
Second, staking enhances security. When over 50% of tokens are staked, it becomes nearly impossible for attackers to control the network. This high participation rate makes attacks costly and impractical. Additionally, staking allows participants to vote on network upgrades. This gives them a voice in shaping the blockchain's future.
Lastly, proof-of-stake systems improve scalability. Some platforms handle over 10,000 transactions per second. This makes them faster and more efficient than traditional proof-of-work systems.
Comparison of Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work
Proof-of-stake and proof-of-work differ in several key areas. Proof-of-stake relies on staked tokens for participation, while proof-of-work requires powerful mining hardware. This makes proof-of-stake more accessible and environmentally friendly. It also consumes 99% less energy than proof-of-work systems.
Metric | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Proof of Work (PoW) |
|---|---|---|
Resource Requirements | Requires tokens for participation | No tokens required for participation |
Hardware Requirements | Less demanding hardware | Requires powerful mining rigs |
Efficiency | More efficient, lower operational costs | High energy consumption and costs |
Finality | Provides true finality | Relies on probabilistic finality |
Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly | High environmental impact due to energy use |
Proof-of-stake systems also offer true finality. Once a transaction is validated, it cannot be reversed. In contrast, proof-of-work relies on probabilistic finality, which can lead to delays. These differences make proof-of-stake a preferred choice for many modern blockchain networks.
How Does Staking Work?

The Role of Validators
Validators are the backbone of proof-of-stake blockchains. They ensure the network runs smoothly by verifying transactions and adding them to the blockchain. Think of them as gatekeepers who maintain the integrity of the system. To become a validator, an individual must stake a certain amount of crypto as collateral. This stake acts as a guarantee of their honest behavior. If a validator tries to cheat the system, they risk losing their staked tokens.
Validators perform several critical tasks:
They validate transactions to ensure they follow the network's rules.
They create new blocks by grouping verified transactions.
They participate in the consensus process, helping the network agree on its current state.
They secure the network by preventing double-spending and other malicious activities.
For example, in a 20-node network, 19 validators might confirm a transaction within 25 seconds. If one validator publishes a competing block, it could cause a slight delay. However, the network resolves these conflicts quickly, ensuring consistency across all validators.
The Staking Process
Staking involves a few straightforward steps. First, participants choose a blockchain network and a staking platform. Then, they lock up their crypto in a wallet connected to the platform. This locked crypto supports the network's operations, such as transaction validation and block creation. In return, participants earn rewards based on their staked amount and the network's reward rate.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how staking works:
Compare reward rates across platforms to find the best option.
Set up a compatible crypto wallet and secure it.
Connect the wallet to the staking platform.
Choose a staking pool based on its fees and reputation.
Stake tokens and confirm the transaction.
Monitor staking performance and collect rewards.
For instance, Alice might stake 5 ETH on Ethereum 2.0 using her MetaMask wallet. Each week, she could earn 0.1 ETH as a reward for her contribution to the network.
Lock-Up Periods and Their Importance
Lock-up periods are a key aspect of staking. During this time, participants cannot withdraw or trade their staked tokens. While this might seem restrictive, it plays a vital role in maintaining network stability. By reducing the circulating supply of tokens, lock-up periods help stabilize prices and prevent panic selling during market downturns.
These periods also enhance security. They ensure validators remain committed to the network, reducing the risk of malicious behavior. Additionally, regular staking rewards provide participants with steady returns, even when the market is volatile. For example, Polkadot requires a lock-up period for its staking process, which helps maintain its high staking ratio of 56%.
Lock-up periods may vary across platforms, so participants should understand the terms before staking. While they offer benefits like price support and network security, they also limit liquidity. This trade-off is something every participant should consider carefully.
How Much Can I Earn?
Staking offers a unique opportunity to earn passive income, but the potential rewards depend on several factors. These include the cryptocurrency being staked, the platform used, and the staking ratio of the network. For example, Ethereum staking currently provides returns between 3% and 4%, while Cosmos (ATOM) leads with an impressive 18.5% yield. These figures highlight the wide range of earnings possible in the staking ecosystem.
The table below provides a snapshot of staking rewards for popular cryptocurrencies:
Asset | Reward (%) |
|---|---|
Cosmos | 18.5 |
Ethereum | 3-4 |
Returns from staking often outpace traditional investments. Ethereum, for instance, offers stable returns of around 5.7% to 6%, which is higher than the average annual stock market yield of 4%. This makes staking an attractive option for those looking to grow their crypto holdings.
The potential earnings also vary based on the staking market cap and staking ratio. The table below compares key metrics for popular cryptocurrencies:
Asset | Price (USD) | Reward (%) | Staking Market Cap (USD, Million) | Staking Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethereum | 4.99 | 41,403.84 | 17.59 | |
Solana | 27.43 | 7.19 | 10,650.40 | 70.39 |
Cardano | 0.32 | 3.12 | 7,116.94 | 62.85 |
BNB Chain | 243.61 | 2.21 | 5,482.51 | 14.50 |
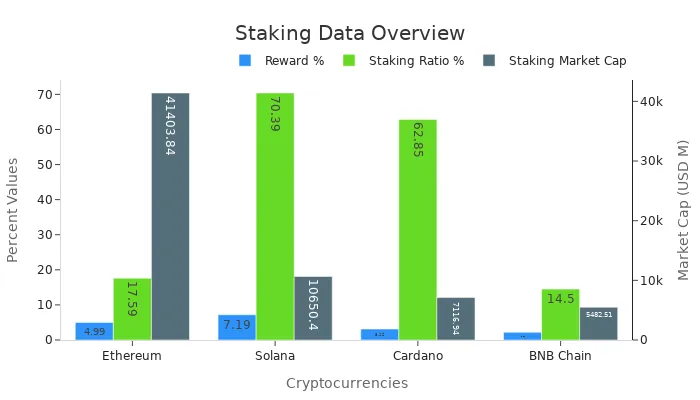
Recent research shows that staking yields can vary significantly. While Cosmos offers high returns, Ethereum provides stability, making it a preferred choice for many investors. The diversity in staking rewards allows participants to choose options that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
By staking, individuals not only earn rewards but also contribute to the security and efficiency of blockchain networks. This dual benefit has made staking a popular strategy for both individual and institutional investors. So, how much can you earn? It depends on your chosen crypto and staking platform, but the potential for substantial returns is undeniable.
Benefits of Staking
Earning Passive Income
One of the most attractive benefits of staking is its ability to generate passive income. By locking up their crypto, participants earn staking rewards without actively managing their investments. This makes staking an appealing option for those looking to grow their digital assets over time. The annual returns vary depending on the cryptocurrency and platform, with some offering exceptionally high yields.
For example, Algorand provides an impressive 84.19% annual return, while Cardano offers a steady 4.96%. Even platforms like Cake DeFi allow users to earn up to 20% without requiring a minimum deposit. The table below highlights the potential returns from staking:
Token | Annual Return (%) | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|---|
Average | 6.08 | N/A |
Algorand | 84.19 | N/A |
Cardano | 4.96 | 2 ADA |
Cake DeFi | 20 | N/A |
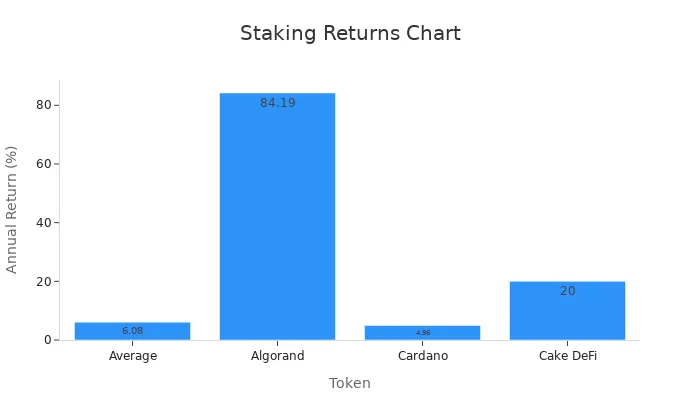
These figures demonstrate how staking can outperform traditional investment options, making it a popular choice for both new and experienced investors.
Contribution to Blockchain Security
Staking plays a crucial role in enhancing blockchain security. When users stake their tokens, they help secure the network by making it harder for malicious actors to gain control. Validators, who are selected based on their staked assets, face economic penalties for dishonest behavior. This system promotes integrity and ensures the network remains trustworthy.
Staking enhances security by requiring a significant percentage of tokens to be staked, making attacks costly.
Validators improve transaction processing efficiency, enabling networks to handle thousands of transactions per second.
Economic penalties discourage dishonest actions, fostering a reliable ecosystem.
For instance, validators in proof-of-stake systems perform three critical functions: verifying transactions, proposing new blocks, and maintaining network security. This process not only strengthens the blockchain but also ensures its scalability and efficiency.
Accessibility and Ease of Use
Staking has become increasingly accessible, attracting a broader range of participants. Many platforms now offer user-friendly interfaces that simplify the staking process. Investors can stake their crypto with just a few clicks, even if they lack technical expertise.
The updates to staking platforms focus on simplicity and accessibility. Lower staking thresholds and intuitive interfaces make it easier for beginners to participate. Platforms also handle technical aspects like blockchain syncing, allowing users to stake with confidence.
Additionally, 24/7 customer support ensures that users receive assistance whenever needed. These improvements make staking an excellent entry point for those new to crypto while providing seasoned investors with a hassle-free way to diversify their portfolios.
Risks of Staking
Cryptocurrency Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices are notoriously unpredictable. This volatility can significantly impact staking outcomes. When the market is bullish, staked tokens often gain value, leading to higher rewards. However, during a bear market, the rewards might not offset the losses caused by falling token prices. For instance, staking rewards in a bull market could result in net gains, but in a bear market, the same rewards might lead to net losses.
Market Condition | Effect on Staking Outcomes |
|---|---|
Bull Market | Staking rewards increase in value as token price appreciates, leading to higher net gains. |
Bear Market | Staking yields may not compensate for significant price drops, resulting in net losses. |
High Volatility | Newer networks may experience extreme price swings, affecting the stability of staking rewards. |
Investors should consider the market's condition before staking. While staking offers passive income, the value of the rewards depends on the token's price stability.
Lock-Up Periods and Liquidity Risks
Lock-up periods are a double-edged sword in staking. On one hand, they stabilize the network by ensuring participants remain committed. On the other hand, they limit liquidity, which can be risky during market fluctuations. Most proof-of-stake networks enforce lock-up or unbonding periods, ranging from days to weeks. During this time, staked tokens cannot be accessed or traded.
Longer lock-up periods often yield higher rewards but restrict access to funds.
Standard unbonding periods last 3-4 weeks, leaving investors unable to react to sudden market changes.
The immobility of staked tokens can result in missed opportunities during price surges.
For example, Polkadot offers attractive rewards but requires a lock-up period, which might deter those who need quick access to their funds. Participants should weigh the benefits of higher returns against the risk of reduced liquidity.
Platform Security Concerns
Staking platforms are not immune to security risks. Validators can face slashing penalties if they violate network rules, leading to a loss of staked assets. Additionally, smart contract vulnerabilities have resulted in significant losses in the past. For instance, a $160 million hack on Euler highlighted the risks of poorly secured platforms.
Security Concern | Description |
|---|---|
Slashing | Validators can lose portions of staked assets due to network violations. |
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities | Exploits have led to significant losses, e.g., $160 million hack on Euler. |
Custodial Risks | Centralized platforms have risks, as seen with BlockFi and Celsius failures. |
Centralized platforms also pose custodial risks. Users may not own the actual crypto but instead hold IOUs, which can become worthless if the platform fails. Regulatory actions, like the SEC's fine against Kraken, further emphasize the importance of choosing trustworthy platforms. Investors should prioritize security when selecting a staking platform to protect their assets.
How to Get Started with Staking
Choosing a Staking Platform
The first step to get started with staking is selecting the right platform. With so many options available, it’s essential to evaluate platforms based on reward rates, security features, and ease of use. For instance, Kraken offers up to 13% APY, while Binance provides as much as 33% APY. However, higher rewards often come with increased risks, so users should also consider validator performance and platform security.
A reliable staking platform should have strong security measures, flexible withdrawal options, and low fees. Platforms like Kraken and Binance excel in these areas, but users should also look for accessible interfaces and responsive customer support. Diversifying across multiple platforms can further reduce risks and maximize rewards.
Selecting a Cryptocurrency
Choosing the right cryptocurrency is just as important as picking a platform. Popular options like Ethereum, Cardano, and Polkadot offer varying reward rates and lock-up periods. For example, Ethereum staking yields around 4% annually, while Cosmos offers up to 18.5%. Beginners should consider factors like market volatility, staking ratios, and the project’s long-term potential.
It’s also crucial to acquire the cryptocurrency through trusted exchanges like Binance or Coinbase. Once purchased, users can transfer their crypto to a staking wallet and begin earning rewards. Diversifying across multiple cryptocurrencies can help balance risks and returns.
Understanding Staking Terms
Before diving into staking, users should familiarize themselves with key terms. Lock-up periods, for instance, refer to the time during which staked tokens cannot be withdrawn. These periods vary by network and can impact liquidity. Validators are another critical concept—they are responsible for securing the network and validating transactions.
Other terms like slashing penalties, staking pools, and smart contracts also play a role in staking operations. For example, slashing penalties occur when validators act dishonestly, leading to a loss of staked assets. Understanding these terms helps users make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Starting the Staking Process
Getting started with staking might seem complicated, but it’s actually a straightforward process. Whether someone is new to crypto or already familiar with blockchain networks, following a few simple steps can help them begin earning rewards. Here’s a step-by-step guide to kick things off:
Choose a Staking Platform: Start by selecting a reliable platform that supports the desired cryptocurrency. Popular options include Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase. Look for platforms with competitive reward rates, strong security, and user-friendly interfaces.
Acquire Cryptocurrency: Purchase the crypto you want to stake through a trusted exchange. For example, if you plan to stake Ethereum, buy at least 32 ETH, as this is the minimum requirement for becoming a validator.
Set Up a Wallet: Transfer your crypto to a compatible wallet. Many platforms provide staking wallets, but hardware wallets like Ledger offer extra security.
Deposit to the Network: For Ethereum staking, generate validator keys and send a signed deposit message with at least 32 ETH to the deposit contract. This step ensures your funds are locked into the network for staking.
Wait for Activation: New validators must go through an activation queue before they can start validating transactions and earning rewards. This process ensures the network remains stable and secure.
Monitor and Earn Rewards: Once activated, your staked crypto begins earning rewards. Keep an eye on your staking performance through the platform’s dashboard. Some platforms even allow you to compound your rewards by restaking them.
Tip: Beginners might prefer staking pools, which allow users to stake smaller amounts of crypto and share rewards with other participants. This option reduces the technical complexity of staking.
By following these steps, anyone can start staking and contribute to the security of blockchain networks. It’s a great way to grow crypto holdings while supporting decentralized systems.
Popular Cryptocurrencies for Staking

Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is one of the most popular cryptocurrencies for staking. Its transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) has made it a top choice for both individual and institutional investors. With over one million active validators as of late 2023, Ethereum showcases a strong and growing staking ecosystem. Participants can earn an average annual reward of 4.99%, making it a reliable option for those seeking steady returns.
Ethereum’s staking market cap stands at an impressive $41.4 billion, reflecting its dominance in the crypto world. Validators play a crucial role in securing the network, and the increasing number of participants highlights the trust in Ethereum’s staking mechanism. Platforms offering liquid staking have further simplified the process, allowing users to earn rewards while maintaining access to their funds.
Asset | Price (USD) | Reward (%) | Staking Market Cap (USD, Million) | Staking Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ethereum | 1,925.74 | 4.99 | 41,403.84 | 17.59 |
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano stands out for its high transaction speed and energy-efficient design. It offers an average return on stake (ROS) of 4.5% to 5.5%, making it an attractive option for staking enthusiasts. Cardano’s staking pools are known for their reliability, with top-performing pools producing over 16,000 blocks. This consistency ensures participants can earn rewards without worrying about network downtime.
To maximize returns, users should target pools with saturation levels between 30% and 80%. Pools exceeding 95% saturation often see diminished rewards. Cardano’s staking mechanism is designed to be user-friendly, allowing participants to stake their ADA tokens directly from their wallets without needing advanced technical knowledge.
Tip: Avoid pools advertising yields above 10%, as they may not be sustainable in the long run.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot focuses on scalability and interoperability, making it a unique option for staking. It offers a competitive yield of 11.5%, with a staking ratio of 56%. Approximately 853.2 million DOT tokens, valued at $3.7 billion, are currently staked. This high level of participation reflects the confidence users have in Polkadot’s network.
Polkadot’s historical rewards rate of 14.88% demonstrates its potential for high returns. Its staking system also supports nominators, allowing users to delegate their tokens to validators. This feature makes staking more accessible to those who may not have the resources to run a validator node themselves.
Cryptocurrency | Yield | Staking Ratio |
|---|---|---|
Cosmos (ATOM) | 18.5% | 59% |
Polkadot (DOT) | 11.5% | 56% |
Ethereum (ETH) | 3-4% | N/A |
Polkadot’s focus on innovation and its robust staking rewards make it a strong contender for anyone looking to earn passive income through staking.
Other Notable Coins
While Ethereum, Cardano, and Polkadot dominate the staking landscape, several other cryptocurrencies offer competitive opportunities for investors. These coins provide unique features and attractive rewards, making them worth considering.
Cosmos (ATOM)
Cosmos stands out as a leader in staking yields, offering an impressive 18.5%. Its high staking ratio of 59% reflects strong community participation and trust in the network. Cosmos focuses on interoperability, allowing different blockchains to communicate seamlessly. This feature has made it a favorite among developers and investors alike. With a total staked value of $1.2 billion, Cosmos continues to attract attention for its scalability and innovation.
Solana (SOL)
Solana has gained popularity for its high performance and scalability. It processes thousands of transactions per second, making it one of the fastest blockchains available. Solana offers a competitive annual percentage yield (APY) of around 7%, appealing to those seeking a balance between returns and network reliability. Its low transaction fees and growing ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) further enhance its appeal.
Avalanche (AVAX)
Avalanche is another notable option for staking. Known for its speed and low energy consumption, it provides an APY of approximately 9%. Avalanche’s unique consensus mechanism ensures quick finality, making it a strong contender in the crypto space. Its focus on decentralized finance (DeFi) and enterprise solutions has helped it carve out a niche among blockchain networks.
A Quick Comparison
Here’s a snapshot of how these coins compare in terms of staking rewards and participation:
Cryptocurrency | Staking Yield | Staking Ratio | Total Staked Value |
|---|---|---|---|
Cosmos (ATOM) | 18.5% | 59% | $1.2 billion |
Solana (SOL) | 7.0% | N/A | N/A |
Avalanche (AVAX) | 9.0% | N/A | N/A |
These coins demonstrate the diversity within the staking ecosystem. Whether someone prioritizes high yields, scalability, or innovative features, there’s a crypto option to match their goals.
Staking offers a unique way to earn rewards while supporting blockchain networks. It allows participants to lock their crypto and contribute to network security, earning a share of newly minted coins or transaction fees. However, staking comes with risks, such as price volatility, lock-up periods, and slashing penalties.
The balance between potential rewards and risks in staking requires careful consideration of individual circumstances, technical capabilities, and risk tolerance.
To make the most of staking, users should research thoroughly. Regularly monitoring validator performance, understanding inflation's impact on real yields, and diversifying across platforms can help mitigate risks. Compound staking strategies can also enhance returns over time.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Potential Returns | Earning a share of newly minted coins or collected fees through staking. |
Significant Risks | Includes price volatility, lockup requirements, and slashing penalties. |
By weighing the potential rewards against the risks, participants can make informed decisions. Staking is a powerful tool for growing crypto holdings, but success depends on understanding the process and managing risks effectively.
FAQ
What is the minimum amount of cryptocurrency needed to start staking?
The minimum amount depends on the blockchain. For example, Ethereum requires 32 ETH to become a validator. However, staking pools let users stake smaller amounts, making it more accessible. Always check the platform's requirements before starting.
Can I lose money while staking?
Yes, staking carries risks. Cryptocurrency prices can drop, reducing the value of your rewards. Validators may also face slashing penalties for dishonest behavior. Research the platform and understand the risks before staking.
How do staking rewards get calculated?
Rewards depend on factors like the cryptocurrency, staking ratio, and network rules. Some platforms offer fixed annual percentage yields (APYs), while others adjust rewards based on network activity. Higher stakes often lead to higher rewards.
Can I unstake my cryptocurrency anytime?
Not always. Many platforms enforce lock-up periods, during which staked tokens cannot be withdrawn. These periods vary by network, ranging from a few days to several weeks. Check the terms before staking to avoid surprises.
Is staking better than mining?
Staking is more energy-efficient and accessible than mining. It doesn’t require expensive hardware or high electricity costs. However, mining might offer higher rewards for those with the right resources. The choice depends on your goals and resources.
Tip: Beginners often find staking easier to start with compared to mining.